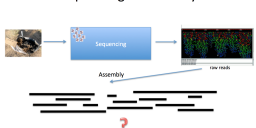
Data Preparation – Metagenome
This post explains what needs to take place before data gets imported into ggKbase. Step 1: Read File Organization Once the sample has been sequenced, you need to slack Rohan and Leylen as a group for download and guidance to rename the read files for processing & QC. Download: It’ll be done in a directory with the…