Keep track of your disk storage footprint on biotite – usage must be monitored. Storage space is not endless — important files should be compressed and intermediate files should be removed.
It is important to not store primary data in your home directory. This storage volume is heavily used and has the ability to impact performance on the entire system. Data and work should be kept on one of the data drives assigned to the project you are working on.
For metagenome project in general, we keep raw sequencing data (read files from a DNA sequencing facility/JGI etc) separate from assembled/derived data (assembly directories, mapping etc).
The common format for this separation of data is to have two directories, “raw.d” and “assembly.d”.
In raw.d, the files remaining should be:
projectname.1.fastq.gz # COMPRESSED; always keep the original files! projectname.1.fastq.gz # COMPRESSED; always keep the original files! projectname_trim_clean.PE.1.fastq.gz # COMPRESSED projectname_trim_clean.PE.2.fastq.gz # COMPRESSED
If the assembly worked and you are in the binning/post-binning stages, projectname_trim_clean.PE.fa may be deleted. Also, projectname_trim_clean.SR.fastq.gz may be deleted unless you have a specific need for it. Fastqc reports may be kept or deleted; these are small files.
In assembly.d, the remaining files should be:
projectname_scaffold.fa.genes.faa-vs-kegg.b6+.gz # COMPRESSED projectname_scaffold.fa.genes.faa-vs-uni.b6+.gz # COMPRESSED projectname_scaffold.fa.genes.faa-vs-uniprot.b6+.gz # COMPRESSED projectname_scaffold.fa projectname_scaffold.fa.16s projectname_scaffold.fa.genes projectname_S1_scaffold.fa.genes.faa projectname_scaffold.fa.genes.fna projectname_scaffold.fa.summary.txt projectname_scaffold.fa.trnascan projectname_scaffold.fa.trnascan.fasta projectname_scaffold_mapped.log begin contig.fa end log mapped.log scaffold.fa
Other files can be deleted, unless you are specifically working with them. This includes the bt2/ directory, projectname_mapped.sam.gz, and projectname_scaffold.16S.cmsearch. Mapping files can always be regenerated.
Useful commands:
How to check disk storage usage?
du -sh ./*
How to compress a file?
gzip filename
How to remove a file?
rm filename
Effectiveness of gzip and rm:
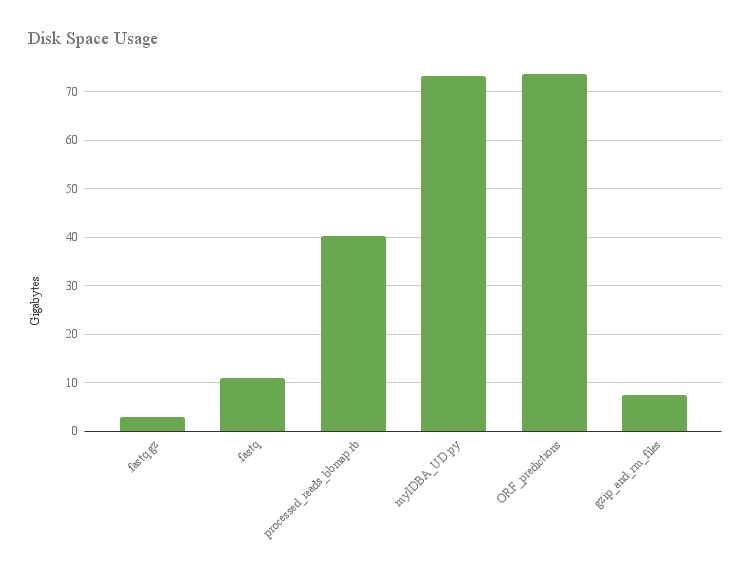
This histogram shows the size of files on biotite while processing raw reads for ggkbase. Compressing and removing files save space!